Under-diagnosis of Bronchiectasis Hinders Treatment
Read More
Bronchiectasis is when the airway walls thicken or enlarge due to chronic inflammation and recurring lung infections. Bronchiectasis damages the airways, which makes it hard for mucus to leave the body. As a result, mucus builds up in the lungs, attracting bacteria and microbes that lead to infection. Recurring infections lead to chronic inflammation, and more mucus buildup. Chronic inflammation causes additional thickening and widening of the airways.
Symptoms of bronchiectasis can take months or even years to develop. Some typical symptoms include:
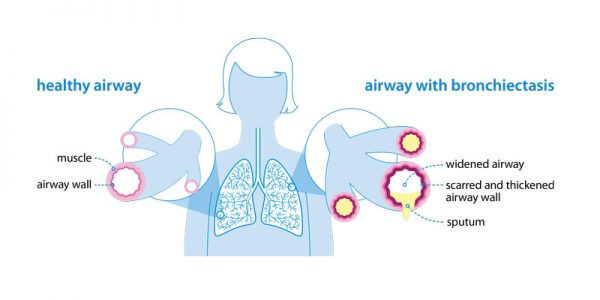
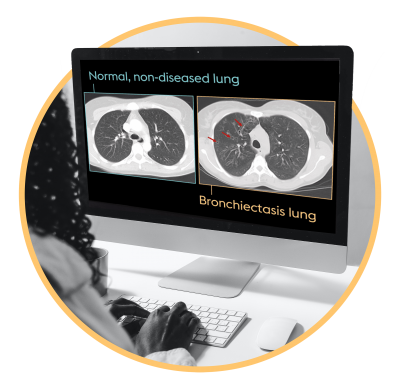
If your physician thinks you have bronchiectasis, some tests will be arranged for you.
Tests your physician may organize include:
Depending on your test results, you may be referred to a pulmonologist, who may arrange additional tests including:
There’s no cure for bronchiectasis, but treatment is important to help manage the vicious cycle of bronchiectasis. The main goal of treatment is to keep infections and bronchial secretions under control. It’s also critical to prevent further obstructions of the airways and minimize lung damage. Common methods of treating bronchiectasis include:
Call us at 1.833.3TACTILE (1-833-382-2845)